Toll was identified in genetic screens exploring the
maternal specification ofbody axes in the Drosophila
embryo. Subsequent studies revealed that Toll is also used
for innate immune signaling and is conserved from insects
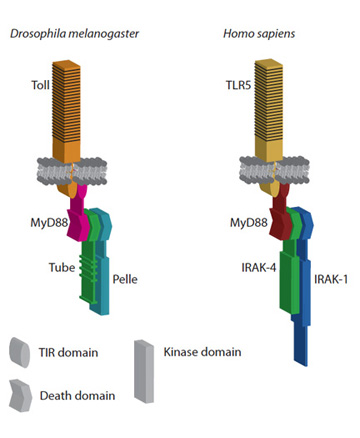
to humans. Three proteins in the Drosophila Toll
pathway – MyD88, Tube, and Pelle – contain a protein
interaction motif called the death domain (first
identified in a programmed cell death pathway). We have
characterized a trimeric complex of these death domains
that transduces signals from Toll to downstream effectors.
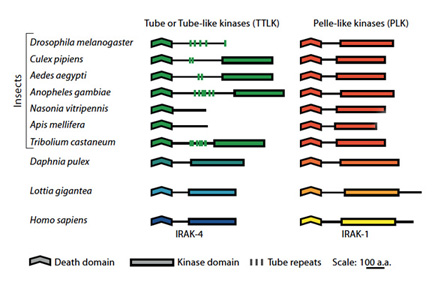
Our demonstration that counterparts of Tube and Pelle
exist across a wide range of animal species (1) led us to
predict that the trimeric architecture of the Drosophila
pathway would be preserved in human (2)s, a
prediction born out by crystallographic studies in the
laboratory of Hao Wu (Cornell).
Recent Research
We extended our studies to explore how formation of the death domain trimer leads to phosphorylation and degradation of the inhibitor protein, Cactus, releasing the NF-kappaB protein Dorsal (and its close relative Dif) to translocate into nuclei and activate transcriptional responses to Toll activation. In particular, we focused on the activity of Pelle as a protein kinase required for signaling downstream of Toll.